Head And Neck Cancer
HEAD & NECK CANCER
General principles and outline of management
History & Clinical Examination :
• Clinical Staging
• Assessment of Performance and Nutrition Status.
• Investigations for histological diagnosis- Biopsy / FNAC / Slide Review
- Goals of Treatment:
Stage I-IVA : Curative
Stage IV B-C : Palliative - Treatment Modalities:
Surgery and radiotherapy are the definitive therapies in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Chemotherapy by itself is not a definitive treatment.
Surgery:
• It is used as a single modality in early disease (stage I & II).
• It is combined with post-operative adjuvant radiotherapy in advanced disease (stage III & IV).
• Wide excision of tumor in all dimensions with adequate margins and appropriate neck dissection is essential in local-regional control of disease.
Radiotherapy:
• External beam radiotherapy and / or brachytherapy are used either as a single modality or as a part of multi-modality treatment.
• Three Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy (3-DCRT)
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) or Image Guided radiotherapy ( IGRT) are useful advances in radiotherapy techniques that can be used in primary treatment with radiation therapy . These techniques allow for better sparing of adjacent critical structures like the spinal cord, parotids thereby enabling better tumor coverage and may help in dose escalation to the target volume.
Chemotherapy:
It is usually used in combination with radiotherapy (sequential or concurrent. Current evidence favors concurrent administration of chemo radiotherapy). It has a role in organ/ voice preservation (in laryngeal / hypo pharyngeal cancers) and in oropharyngeal cancers. In select patients chemotherapy can be used for palliating symptoms.
General guidelines for selecting a treatment modality:
• Stage I / II disease – Single modality (Surgery or RT)
• Stage III & IV disease – Combined modality
Surgery + Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy + radiotherapy
Surgery is preferred over radiotherapy as a single modality in
• Sites where surgery is not morbid (cosmetically and functionally)
• Lesions involving or close to bone – to prevent radio necrosis.
• Young patients – possibility of a subsequent second primary
• Sub mucous fibrosis
RT is preferred over surgery as a single modality, where
• Severe impairment of function / cosmesis with surgery, e.g. base tongue, glottis.
• Surgery is technically difficult with high morbidity and poor results e.g. nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
• Patient refuses surgery / high risk of surgery
Criteria of Unresectability :
Primary disease: Adequate surgical clearance is not achievable
• Extensive InfraTemporal Fossa involvement
• Extensive involvement of base skull.
• Extensive soft tissue disease: skin edema/ ulceration.
Nodal Disease:
• Clinically fixed nodes.
• Infiltration of Internal /Common carotid artery.
• Extensive infiltration of prevertebral muscles, skull base.
Reconstruction options:
• Mucosal defects:
Small defect – local flap / SSG / leave raw
Large defect – Free flap/Pedicle flap (PMMC)
• Skeletal defect – free fibula /cadaveric bone graft /silastic /plate.
• Skin defect – local flap / free flap / deltopectoral flap / forehead flap / PMMC
Indications for post operative radiotherapy:
Primary:
• Large primary – T3 or T4
• Close or positive margins of excision
• Deep infiltrative tumor
• High grade tumor
• Lympho-vascular and perineural invasion
Lymph nodes :
• Bulky nodal disease N2 / N3
• Extra nodal extension
• Multiple level involvement
Indications for Brachytherapy (BRT):
• Accessible lesions
• Small (preferably < 3cm) tumors
• Lesions away from bone
• N0 nodal status
• Superficial lesions
Radical Radiotherapy:
Tumor suitable for Brachytherapy
• T1-2 N0: Radical BRT: 60-70Gy Low Dose Rate 192 Iridium Or equivalent doses with fractionated high dose rate.
• T1-3 N0-1: External RT: 56-60Gy/ 28-30#/ 6 wks
• Boost BRT: Low dose rate 192Iridium: 15-20Gy or
• High Dose Rate: 14Gy in 4 fractions over 2 days (4-3-3-4 Gy)
External RT: 66-70Gy/33-35# /6-7 wks (reducing fields)
Post-operative radiotherapy:
• Primary and nodal disease: 50-60 Gy/25-30 fr/5-6 weeks, using reducing fields.
• Site of residual disease, positive cut margins: 4-10 Gy Boost
Trend towards the use of adjuvant post-operative concomitant CT + RT for patients with high risk factors.
Rehabilitation:
• Abstinence from tobacco/ Alcohol
• Oral Hygiene
• Shoulder physiotherapy in all cases of neck dissections
• Bite guide prosthesis following mandibulectomy
• Jaw stretching exercises to prevent post-operative trismus
• Swallowing and speech rehabilitation
Follow up:
• Every two to three months for first 2 years.
• Six monthly for next 3 years.
• Annually thereafter.
– On every follow up thorough head and neck examination for locoregional control, second primary tumor and late sequelae of treatment.
– Investigation only if indicated by symptoms and positive clinical findings.
– Serum T3 T4 TSH annually particularly for larynx patients.
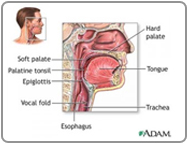
- Oral Cavity
- Lip
- Buccal mucosa
- Lower alveolus
- Retro molar trigone
- Oral tongue
- Floor of mouth (FOM)
- Upper alveolus
- Hard palate
LIP
T1, T2 Tumors: Surgery or RT
Primary:
Surgery: Wide excision
Radiotherapy: Radical Radiotherapy / Brachytherapy.
Nodes
N0: Observe or SOHD
N+: MND / RND
Note: Post op RT as per earlier guidelines.
T3, T4 Tumors: Surgery + Post operative RT/ CT-RT
Primary:
Surgery: Wide excision with marginal/ segmental / hemi mandible resection if required with reconstruction.
Nodes
N0: SOHD followed by FS, if positive nodes MND is required
N+: MND / RND
Note: Bilateral neck needs to be addressed if the primary disease is in midline or extending across midline (including middle third mandible).
Post op RT/CT-RT as per earlier guidelines.
Buccal Mucosa
T1, T2 Tumor’s:
Primary:
Surgery: wide excision +/- marginal mandibulectomy or margins.
Radiotherapy: Radical RT/ Brachytherapy.
Nodes
N0: Observe or SOHD (if cheek flap is raised, USG suspicious, thick tumor or poor follow up expected) followed by FS, if positive nodes, MND is required
N+: MND / RND
Note: Post op RT as per earlier guidelines.
T3, T4 Tumor’s:
Surgery + Post operative RT or CT-RT
Primary:
Surgery: Composite resection of the buccal mucosa with mandible or upper alveolus or overlying skin with reconstruction
Nodes
N0: SOHD followed by FS, if positive, nodes MND is required
N+: MND / RND
Note: Post op RT/ CT-RT as per earlier guidelines.
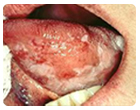
Oral Tongue & Floor of Mouth:
T1, T2 Tumors:
Primary:
Surgery: Wide Excision Glossectomy / Hemiglossectomy
Radiotherapy: Radical RT/ Brachytherapy
Nodes
N0** Observe/ Elective MND (criteria listed below)#
N+ MND/ RND
Note: Post op RT/CT-RT as per earlier guidelines.
T3, T4 Tumor’s:
Surgery + Post operative Radiotherapy
Primary:
Surgery: Appropriate wide / total glossectomy with mandibular swing or pull through along with lingual plate / segmental / hemimandibular resection, if required (based on extent of involvement)
Nodes
N0: SOHD / MND / RND
N+: MND / RND
Note: Bilateral necks need to be addressed if the primary disease is in midline or extends across midline (including middle third mandible).
Post op RT/CT+RT as per guidelines.
Note: Post op RT as per earlier guidelines.
Lower Alveolus & Retro Molar Trigone Mandible uninvolved or minimally involved:
Primary:
Surgery: Wide Excision with marginal mandibulectomy (avoided in RMT disease, edentulous mandible, paramandibular disease, post radiotherapy)
Nodes
N0: Observe or SOHD (if cheek flap is raised, USG suspicious, thick tumor or poor follow up expected) followed by FS, if positive nodes MND is required
N+: MND/ RND
Mandible Grossly Involved

Surgery + Post operative/ CT-RT
Primary:
Surgery: Wide Excision (cheek flap) with segmental/ hemi-mandible resection
Nodes
N0: SOHD followed by FS, if positive nodes, MND are required
Nodes
N0: SOHD / MND / RND
N+: MND / RND
Note: Bilateral necks need to be addressed if the primary disease is in midline or extends across midline (including middle third mandible).
Post op RT/ CT-RT as per earlier guidelines.
Orfit cast for external beam radiotherapy
Maxillary antrum not involved
Upper alveolectomy / Partial maxillectomy
Radical RT / Brachytherapy for selected early T1-2 Hard palate lesions
Maxillary antrum involved
Orbital floor preserving total maxillectomy
Post operative RT/ CT-RT as per guidelines mentioned earlier.
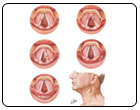
• Base of tongue
• Tonsil
• Soft palate
• Pharyngeal wall
Treatment options:
Stage I & II ( T1-2 N0 )
• Radical Radiotherapy : In most cases.
• Surgery: In selected cases eg. Lateralized lesion, infiltrative disease. (Criteria: Patient’s preference, institutional practice and complexity of procedure).
• Concomitant CT plus RT, followed by neck salvage if residual nodes or as a planned procedure. • Split therapy: (In selected cases of large nodes with small radio-curable primary) Node mass excision followed by RT / CT+RT. T3-4, N0, N+
• Concomitant CT plus RT : In most cases.
• Surgery: (if low peri-op risk & reasonable functional outcome) Composite resection + appropriate neck dissection + Post-operative radiotherapy
• Note: Post-op RT / CT+RT as per general guidelines.
Larynx And Hypopharynx
Larynx:
• Supra-glottis: Epiglottis, Ary-epiglottic folds, Arytenoids, False cords, Ventricles.
• Glottis: True vocal cord with anterior & posterior commissure.
• Sub glottis.
Hypo pharynx:
• Pyriform sinus
• Post-cricoid region
• Posterior pharyngeal wall
Supraglottis:
Surgery is preferred over radiotherapy in cases with
• Large volume disease.
• Cartilage erosion.
• Bulky nodal disease.
• Gross pre epiglottis space involvement
• General condition not permitting concurrent chemo radiotherapy
• Post operative RT as per guidelines mentioned earlier
Glottis
Stage III – T1-2 N1 / T3N0-1
• Concomitant CT+RT
• Surgery: Vertical Partial Laryngectomy/ Near-Total laryngectomy / Total laryngectomy + RT
• Radical radiotherapy in patients with low GC/poor performance status who might not tolerate CT+RT
Stage IV – T4a N0-1 / T1-4aN2-3
• Surgery: Near-Total laryngectomy / Total laryngectomy + RT
• Concomitant CT+RT
• Radical radiotherapy in patients with low GC/ poor performance status who might not tolerate CT+RT
Pyriform Fossa
• Radical Radiotherapy
• Partial Laryngo-pharyngectomy
• Endoscopic laser resection in select cases.
• T1-2 No,1
• T1-2 N2-3
• Concurrent CT+RT.
• Radical Radiotherapy Salvage surgery (Low GC – unable to tolerate CT+RT).
• Split Therapy – Neck dissection + Radical Radiotherapy to primary and neck. T3-4, Any N
• Near-Total Laryngectomy /Total laryngectomy + Partial pharyngectomy + Post operative Radiotherapy.
• Reconstruction of defect depends on mucosal defect. If mucosa adequate – primary closure, if mucosa inadequate – patch PMMC or free radial forearm flap.
• Concurrent CT + RT.
• Radical radiotherapy salvages surgery (Low GC –unable to tolerate CT+RT).
Post Cricoid & Posterior Pharyngeal Wall
• T1-2 N0-1
• Radical Radiotherapy
• T3-4 Any N: Small volume disease
• Concurrent CT+RT.
• Radical Radiotherapy Salvage surgery (Low GC –unable to tolerate CT+RT)
• T3-4 Any: Large volume disease.
• Total laryngo-pharyngo-esophagectomy with gastric pullup or Free jejunal flap or tube pectoralis myocutaneous flap and Post operative Radiotherapy.
Nasopharyngeal Carcinomas
• Treatment options
• T1 / Selected T2 N0 :
• Radical Radiotherapy alone with or without Intraluminal Brachytherapy
• IMRT or 3-DCRT maybe used when facilities are available.
• T3-4 N0 / Any T N+
• Concurrent chemoradiotherapy
• Neo Adjuvant CT x 2 cycles + Concurrent CT + RT
Nasal Cavity & Paranasal Sinuses
• Nasal Cavity
• Maxilla
• Ethmoids
• Frontal Sinus
• Sphenoid

Maxillary Sinus
Treatment of Primary:
T1, T2:
Surgery + Post-op Radiotherapy
• Infrastructure maxillectomy
• Maxillectomy with orbital plate preservation
• RT in case of margin positivity or perineural spread
T3:
• Surgery + Post op Radiotherapy
• Total Maxillectomy with Ethmoidectomy
• Orbital exenteration if eye involved.
T4a:
• Combined craniofacial resection + Post op Radiotherapy.
• CT+RT in unrespectable tumors
T4b:
• Palliative – RT or CT
• Concurrent CTRT may be considered in patient with extremely good performance status.
• Resection in very select group with favorable histology tumors for eg. Adenoid cystic carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma.
• Treatment of Neck
• N0 Observe
• N+ Appropriate neck dissection and post-operative radiotherapy.
